Overview
This project was the final project for CS 3200: Introduction to Databases, created with Annabelle Peak, Trisha Chennuru, and Zahra Wibisana. The course focused on relational databases, understanding how to gather initial requirements and data to building full conceptual and logical models in MySQL. Throughout the semester, we learned about important frameworks, normalization and best practices, advanced programming concepts, like stored procedures and triggers, and most importantly how to turn raw data into clear, actionable insights.
The Vision
Music is something that transcends languages or borders and is used in everyday life, whether walking to class or dancing in a club. We were inspired by how music connects all sorts of people, and wanted to build our application to highlight this impact. So, we decided to develop a database application that centers itself around connecting people through music. This application aims to analyze users’ music profiles and listening histories to identify similarities, differences, and trends in musical tastes with friends, family, and global users.
The Goals
The application's purpose was to analyze users' music profiles and listening histories to identify similarities, differences, and trends in musical tastes. The analytical focus was divided into three key areas:
Personal Insights: Analyzing individual habits such as genre diversity, top artists, and listening streaks.
Social Connections: Revealing musical similarities and differences between connected users (friends/family).
Global Comparisons: Contextualizing personal tastes within country-wide and global trends.
Designing the Database Model
Modeling in MySQL
The database was modeled using MySQL Workbench to create a flexible, relational schema capable of generating meaningful insights from streaming history.
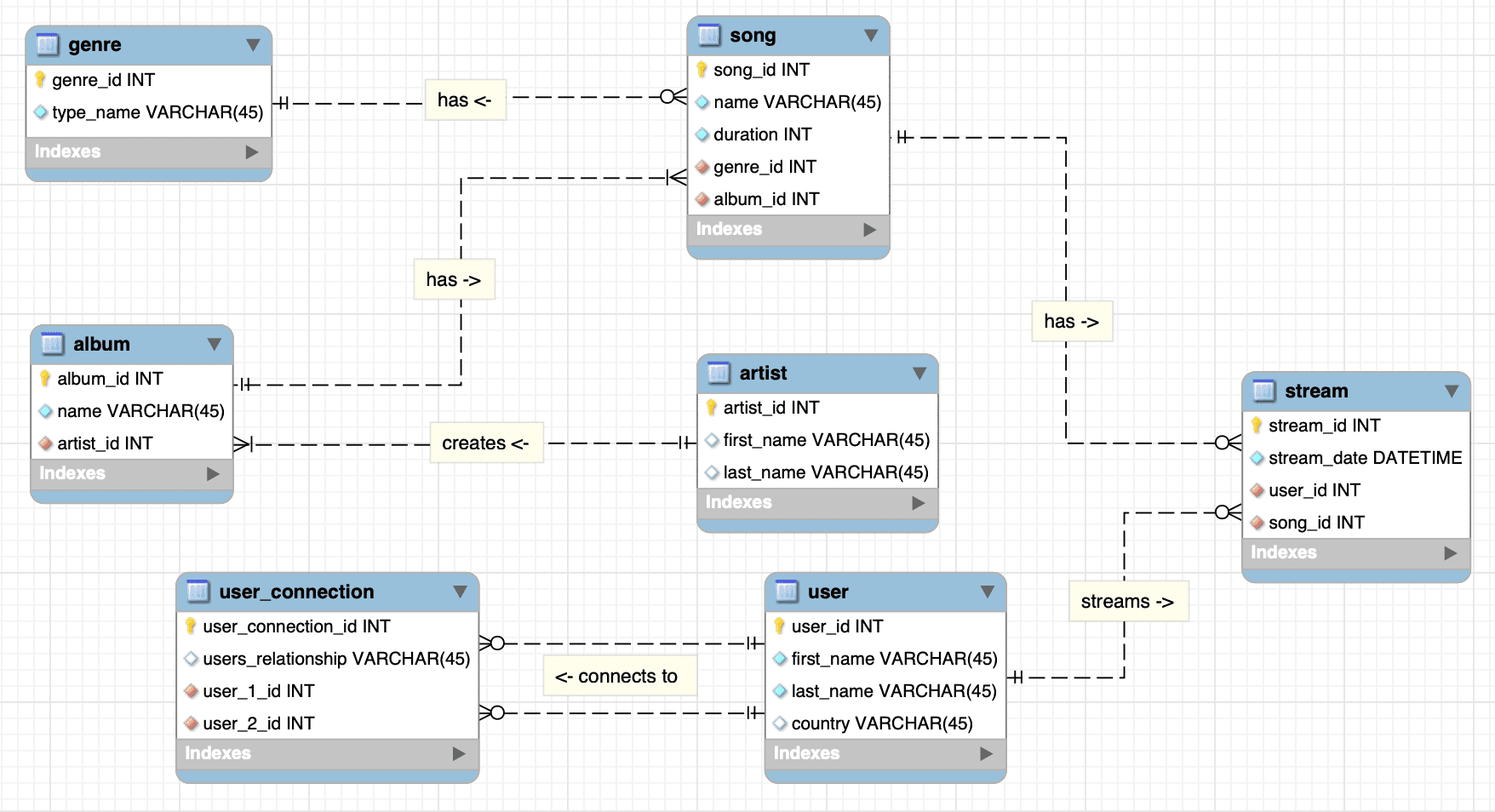
Core Entities & Relationships
The schema was built around seven core entities:
user: Stores user details and their country of residence.artist,album,song,genre: Standard relational tables for music content.user_streams: The central fact table, tying a single stream event to auser, asong, and a precisestream_date(date/time).user_connections: A many-to-many relationship table that links two users (user_1,user_2) and defines their relationship (e.g., "Friends" or "Family").
The design intentionally focused on scalability, making it suitable for future integration with data from external sources like Spotify and Apple Music.
Engineering the Use Cases
We developed various SQL queries. From there, we chose 10 specific queries. We have questions regarding users’ own streaming habits and how they compare to other users and globally. We utilized subqueries, joins, ordering, triggers, stored procedures, aggregation, and temporal analysis. Below are 3 example use cases:
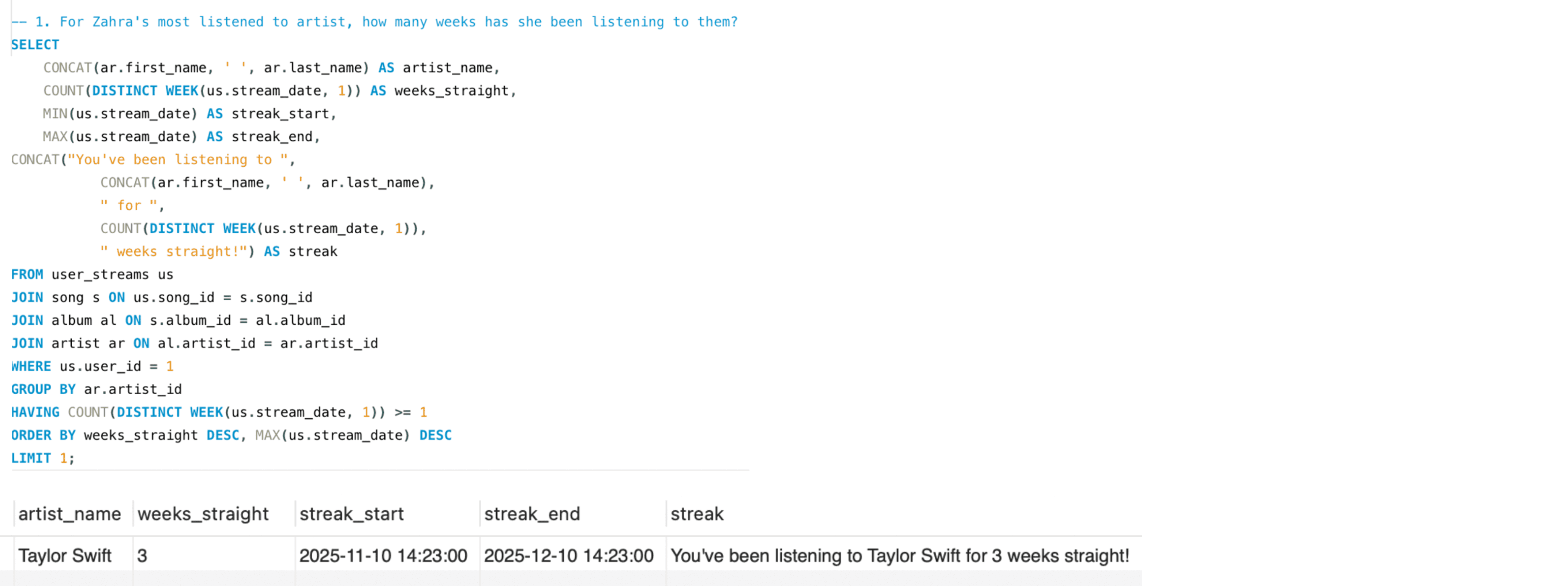
Personal Listening
How many consecutive weeks has Zahra been listening to her most-streamed artist?
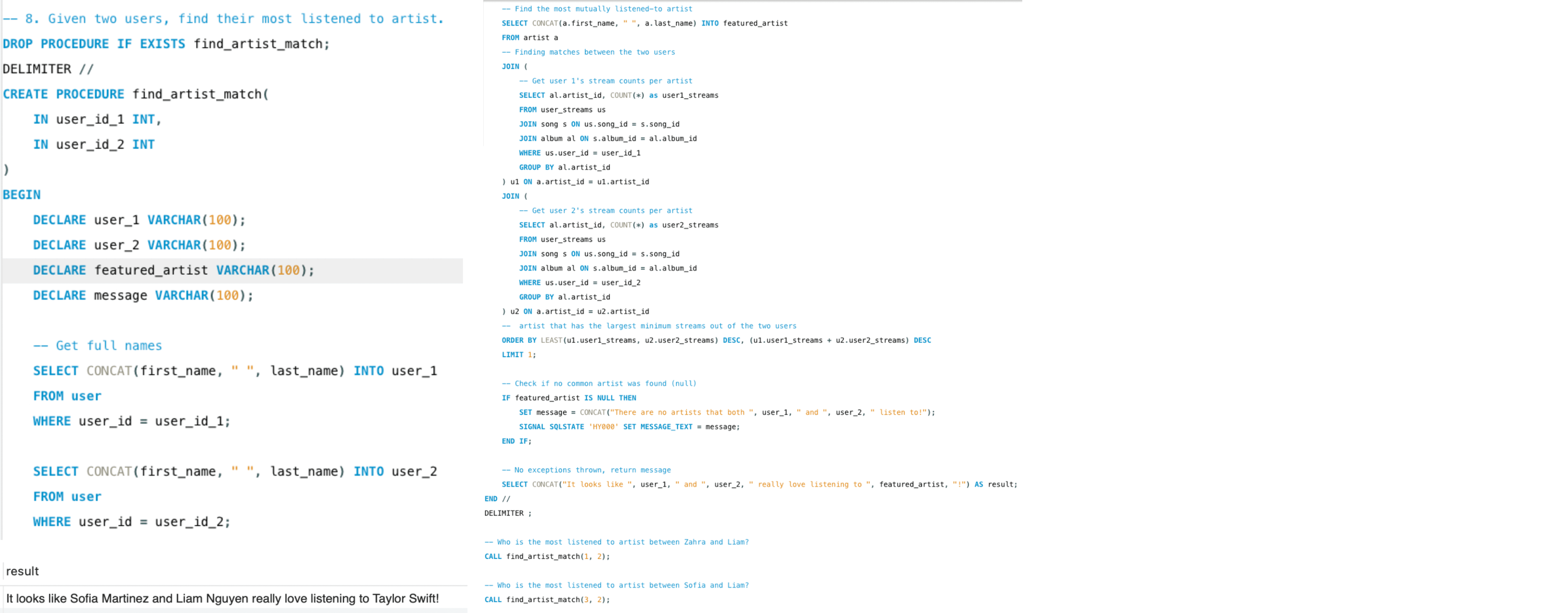
Connections Between Users
Between Liam and Sofia, which artist have they both streamed the most?
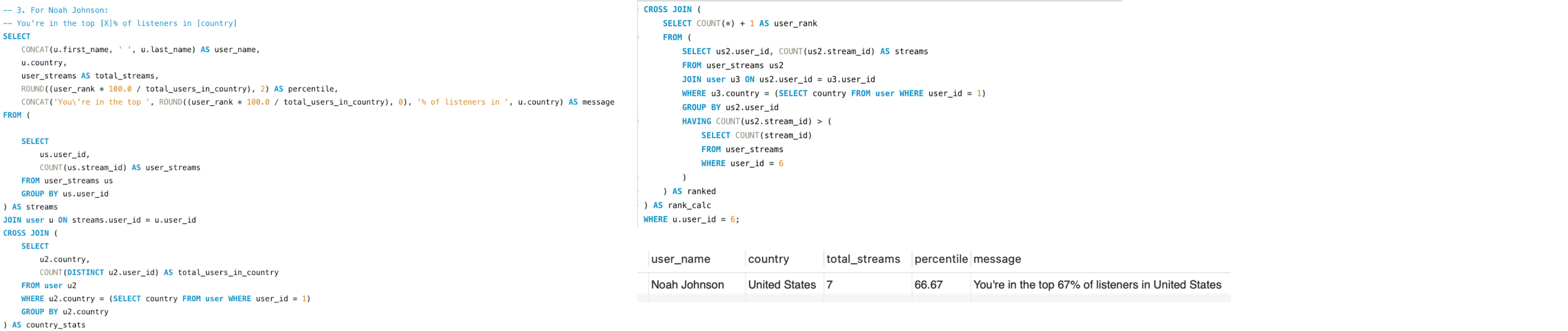
Global Perspective
Where does Noah Johnson rank, in terms of total streams, among other listeners in their country?
Why this Analysis Matters
Turning Data into Connection
Humanizing the Data: We transformed raw timestamps into relatable stories, like finding a "musical match" between friends or tracking a dedicated listening streak.
Defining Relationships: Through many-to-many link tables, the database revealed musical overlaps and patterns.
Core Database Concepts
Smart Structuring: We used Normalization to organize data across seven tables, ensuring every play event was accurate and reduncancy-free.
The Main Table: Our
user_streamstable acted as the heartbeat of the project, letting us pull personal, social, and global insights from one central source.Automated Logic: We created Stored Procedures and Triggers to handle some use cases, like cross-referencing two histories to find a mutual favorite artist.
Future-Proofing: By building a flexible relational model, we created a foundation that can easily scale to handle real data from platforms like Spotify or Apple Music.
What I Learned
Building this project from scratch and creating a database with a team was a great learning experience. I loved the challenge of turning raw, messy streaming data into answers applying different SQL concepts. Moving beyond lecture notes, I saw firsthand how thoughtful data modeling can transform technical work into a meaningful lens for analyzing personal habits and creating social connections.
